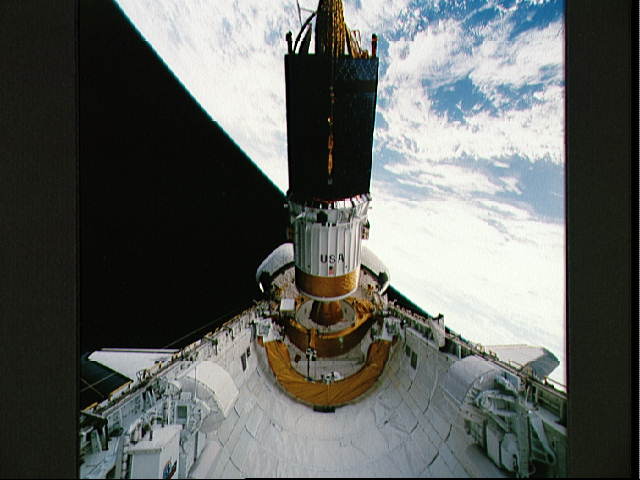
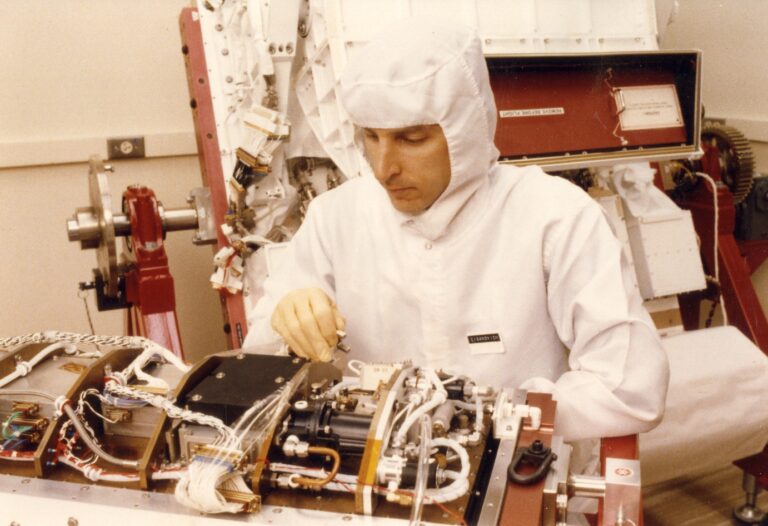
DXS: Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer (DXS)
The Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer (DSX) was a Spacelab payload. It flew as an attached Shuttle payload on the STS-54 mission, which was launched from the Kennedy Space Center on Wednesday, 13 January 1993, and landed at Edwards Air Force Base on Tuesday, 19 January 1993.
DXS consisted of a pair of Bragg crystal spectrometers that employed position-sensitive proportional counters as the X-ray detectors. For the past 25 years, the low energy X-ray diffuse background has been interpreted as thermal emission from a hot plasma in the interstellar medium, but there was no direct proof of its thermal nature. The primary scientific objective of the DXS experiment was to determine if the low energy x-ray diffuse background emission was thermal by determining if there were emission lines in its spectrum. Other important objectives were to determine if the plasma was in thermal equilibrium, to find the temperature of the plasma, to learn which chemical elements were the dominant emitters, and to determine the degree of depletion or enrichment of these elements in the emitting plasma relative to “standard” cosmic abundances.
From Spacelab Diffuse Soft X-ray Bragg Spectrometer (DXS) [Final Report]
Investigators
- Dr. Wilton T. Sanders Space Science and Engineering Center (SSEC)
Related Websites
Publications
-
Diffuse X-Ray Spectrometer (DXS): DXS mission and CDR review. [Greenbelt, MD], National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), Goddard Space Flight Center, 1992. Unpaged. NASA 1.102:992.
-
Gregory, Terri. DXS press coverage: 31 December 1991 to present. Madison, WI, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Space Science and Engineering Center, 1993. Unpaged. UW SSEC Publication No.93.04.D1.
-
Sanders, W. T. and Edgar, R. J. The Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer Experiment. In The X-ray background. Cambrige, UK; New York, NY, Cambridge University Press, 1992, pp297-301. Reprint #1933.
-
Sanders, W. T. and Paulos, R. J. Spacelab Diffuse Soft X-ray Bragg Spectrometer (DXS). Final report NASA Contract NAS 5-26078. Madison, WI, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Space Science and Engineering Center (SSEC), 1996. 31p. UW SSEC Publication No.96.03.S1.
-
Sanders, W. T.; Edgar, R. J.; Juda, M.; Kraushaar, W. L.; McCammon, D.; Snowden, S. L.; Zhang, J., and Skinner, M. A. The Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer Experiment. EUV, X-ray, and Gamma-ray Instrumentation for Astronomy III, San Diego, CA, 22-24 July 1992. Proceedings. Bellingham, WA, SPIE-International Society for Optical Engineering, 1992, pp60-71. Reprint #1879.
-
Sanders, W. T.; Edgar, R. J.; Juda, M.; Kraushaar, W. L.; McCammon, D.; Snowden, S. L.; Zhang, J.; Skinner, M. A.; Jahoda, K.; Kelley, R.; Smale, A.; Stuahle, C., and Szymokowiak, A. Preliminary results for the Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer. EUV, X-ray, and Gamma-ray Instrumentation for Astronomy IV, San Diego, CA, 12 July 1993. Proceedings. Bellingham, WA, SPIE-International Society for Optical Engineering, 1993, pp221-232. Reprint #5406.
-
Sanders, W. T.; Edgar, R. J., and Liedahl, D. A. DXS spectra of the 0.25 keV diffuse background. ‘Rontgenstrahlung from the Universe: Proceedings. Garching, Germany, Max-Planck-Institut fur extraterrestrische Physik, 1996, pp339-340. Reprint #4563.
-
Sanders, W. T.; Edgar, R. J.; Liedahl, D. A., and Morgenthaler, J. P. The soft X-ray background spectrum from DXS. The Local Bubble and Beyond, Lyman-Spitzer Colloguium, Proceedings of the IAU Colluguium No.166, Garching, Germany, 21-25 April 1997. Berlin, Springer-Verlag, 1998, pp83-90. Reprint #4564.
-
Sanders, W. T.; Edgar, Richard J.; Kraushaar, W. L.; McCammon, D., and Morgenthaler, J. P. Spectra of the 1/4 keV diffuse background from the Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer Experiment. Astrophysical Journal v.554, 2001, pp694-709. Reprint #2907.