Hubble Space Telescope High-Speed Photometer (HST HSP)
The high-speed photometer (HSP) was built by the Space Science and Engineering Center (SSEC) and included on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) when it was launched on 25 April 1990. The HSP was replaced early in the mission with COSTAR (Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement) in order to correct an aberration in the primary mirror for the remaining instruments.
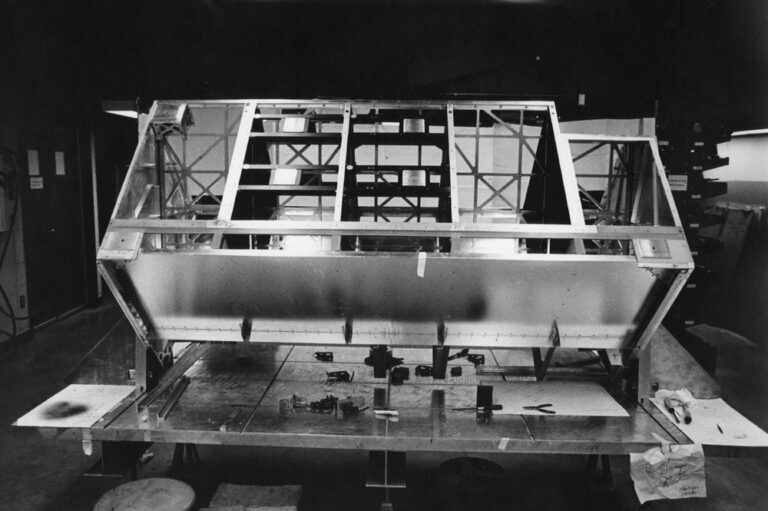
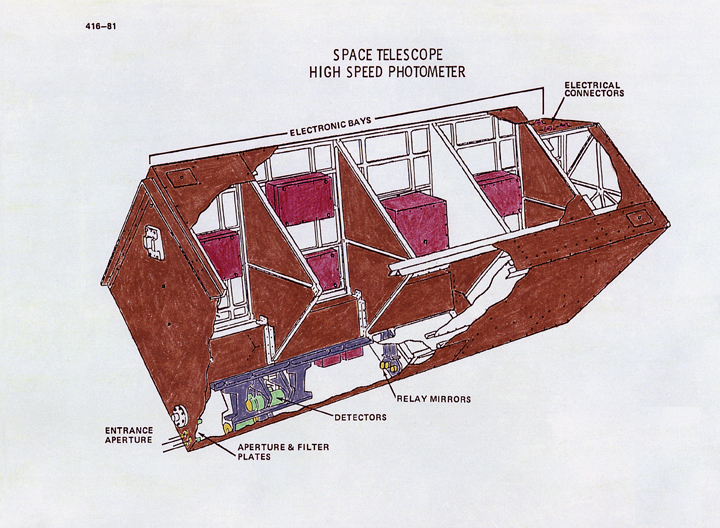
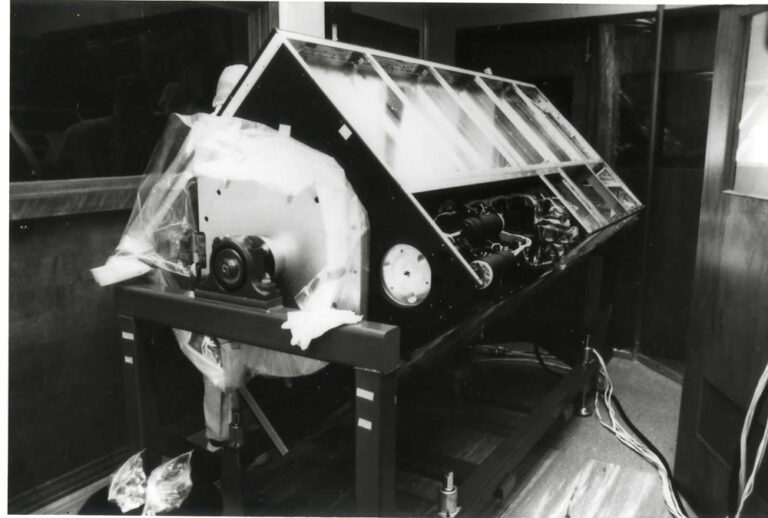
The HSP investigation made fast-time-resolution (down to 10 microseconds) photometric observations of rapidly varying objects in the spectral range 1150 to 8700 A and linear polarimetric observations from 2100 to 7000 A of a wide variety of objects. It established an accurate link between observations made on existing visual and UV photometric systems and the corresponding observations of the objects observed by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Faint Object Camera. The instrument consisted of four image dissectors: two sensitive in the UV and solar blind, the others sensitive in the visible and near infrared. A wide variety of bandpasses were formed by broadband and interference filters arranged in strips near the HST focus. Some of the filters were coated with a polarizing material. Apertures provided a choice of three fields of view: 0.4, 1.0, and 10.8 arc-s. The dissectors could be commanded to receive photoelectrons from any of the approximately 100 filter-aperture-polarizer combinations available.
From National Space Science Data Center, NSSDC ID: 1990-037B-06
Investigators
- Dr. Robert C. Bless Astronomy Department
Related Websites
Publications
-
Bless, R. C.; Richards, E. E.; Bosh, A.; Dolan, J. F.; Elliot, J. L.; Nelson, M.; Percival, J. W.; Robinson, E. L.; Taylor, M.; Van Citters, G. W., and White, R. L. The Hubble Space Telescope’s high-speed photometer. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific v.111, 1999, pp364-375. Reprint #2553.
-
The future of space imaging: Report of a community-based study of an Advanced Camera for the Hubble Space Telescope. Brown, Robert A. Baltimore, MD, Space Telescope Science Institute, 1993. ix, 143p. QB/500.268/F87/1993.
-
Hubble space telescope: Media reference guide. Sunnyvale, CA, Lockheed Missiles and Space Company, Inc. (for National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), [1990].
-
The Hubble Space Telescope optical system failure report. [Washington, DC], National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), 1990. Various paging. NAS 1.2:990.
-
National Research Council (US). Assessment of options for extending the life of the Hubble Space Telescope. Washington, DC , National Academies Press, 2005. CD. QB/500.268/A85/2005.
-
Operating the Hubble Space Telescope. Goddard Space Flight Center: A closer look. Greenbelt, MD, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), Goddard Space Flight Center, 1985. 16p. NAS 1.102:985.
-
Richards, Evan; Percival, Jeff; Nelson, Matt; Hatter, Ed; Fitch, John, and White, Rick. Initial performance of the High Speed Photometer. Space Astronomical Telescopes and Instruments, Orlando, FL, 1-4 April 1991. Bellingham, WA, SPIE-International Society for Optical Engineering, 1991, pp40-48. Reprint #1881.
-
Richards, Evan E. Hubble Space Telescope High Speed Photometer orbital verification test report (Contract No.NAS5-24487). Madison, WI, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Space Science and Engineering Center, and Space Astronomy Laboratory, 1991. 37p., charts. [NASA-CR 189322] UW SSEC Publication No.91.11.R1.
-
Richards, Evan E. Hubble Space Telescope High Speed Photometer science verification test report (Contract No.NAS5-24487). Madison, WI, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Space Science and Engineering Center, and Space Astronomy Laboratory, 1992. 82p., charts. [NASA-CR 189322] UW SSEC Publication No.92.07.R1.